CUSTOM WHEEL FACTS — FITMENT
Wheel Width
Choosing the wheel’s width is important. In addition to correct fitment, the wheel’s width also influences handling and ride quality. Always choose a rim width within the range of the tire’s acceptable rim width specifications.
- Choosing a wider rim: increases vehicular stability, steering response and cornering ability. A rule of thumb is to use a rim width 90% as wide as the tread width (not section width) of a performance tire for street applications. This provides a good balance between performance and ride quality. Always be sure that the chosen rim width is within the tire’s range of acceptable rim width specifications.
- Choosing a narrow rim: results in an improvement in ride quality, but may sacrifice the tire’s ultimate performance capabilities.
- Choosing a mid-range rim width: provides a balance between handling capabilities and ride quality.
Warning: According to RMA guidelines, there is danger in installing a tire of one rim diameter on a rim of a different rim diameter. Always replace a tire on a rim with another tire of exactly the same rim diameter designation and suffix letters. For example: a 16″ tire goes with a 16″ rim. Never mount a 16″ size diameter tire on a 16.5″ rim. While it is possible to pass a 16″ diameter tire over the lip or flange of a 16.5″ size diameter rim, it cannot be inflated enough to position itself against the rim flange. If an attempt is made to seat the tire bead by inflating, the tire bead will break with explosive force and could cause serious injury or death.
See Plus Sizing – Wheel Widths for a chart of acceptable wheel widths by tire size
High Performance Wheels
The following are various high performance wheel measurements that play an important role in determining tire and wheel fitment:
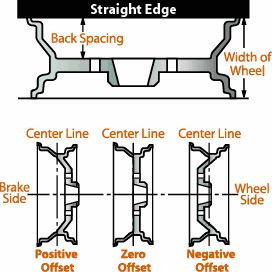
Wheel Backspace
The distance from the back edge of the wheel to the hub mounting surface. To determine the wheel backspace:
- Position the wheel face down.
- Lay a straight-edge across the back of the wheel. Measure the distance from the straight-edge to the wheel’s hub mounting surface.
Wheel Offset
The wheel’s offset is the distance from its hub mounting surface to the centerline of the wheel. The offset of a wheel can be one of three settings:
- Zero offset: The hub mounting surface is even with the centerline of the wheel.
- Positive offset: The hub mounting surface is toward the front or wheel side of the wheel. Positive offset wheels are generally found on front-wheel drive cars.
- Negative offset: The hub mounting surface is toward the back or brake side of the wheel’s centerline. “Deep dish” wheels are typically negative offset. Offset can be calculated by positioning the wheel on a flat surface and measuring its overall width. Subtract the backspace, and divide by two.
Offset = (Width – Backspace) ÷ 2
Bolt Circle
When considering custom wheels for a specific application, it is imperative that the wheel’s bolt circle matches that of the intended vehicle. The bolt circle is the diameter of an imaginary circle formed by the centers of the wheel lugs. The bolt circle reference is designed to accommodate 4, 5, 6 and 8-lug patterns. A bolt circle marked 5-100 (Chevrolet Cavalier, for example) indicates a 5-lug pattern with a diameter of 100mm. Consult the rim manufacturer’s literature for bolt circle information for each application. If there is no information available, you may need to calculate the bolt circle.
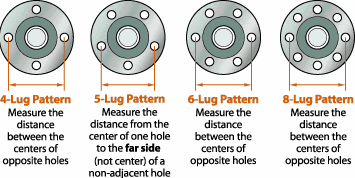
4, 6, or 8-lug patterns:
Record the distance between the centers of two holes directly opposite one another.
5-lug pattern:
Estimate by measuring from the center of one hole to the far side (outside, not center) of a non-adjacent hole. The diagram below illustrates the proper measuring methods.
Hub-Centricity vs. Lug-Centricity
Another important consideration in the proper selection of custom wheels is the concept of hub-centricity. This refers to a situation where the center bore hole of the wheel exactly matches the vehicle’s hub diameter. In other words, if the vehicle’s hub diameter is 56mm (e.g., Acura Integra), the wheel’s center bore hole should be designed to match it perfectly.
Hub-centricity
When automobile manufacturers design a vehicle, they utilize hub-centric wheels so that:
- The wheels are positioned very precisely on the car.
- The possibility of shifting while being mounted is minimized.
Lug-centricity
The alternative to a hub-centric wheel is known as lug-centric.
- The wheels are located solely by the lug nuts rather than the wheel hub.
- As the lug nuts are tightened, they adjust the wheel’s position relative to the hub, thus centering the wheel.
- Properly torqued, the lug nuts continue to keep the wheel centered as the vehicle is driven.
